Relic point Vietnam
Việt NamBLACK ROCK MILL
Go Da Den is a training and discharge location for Tay Son insurgents, formerly located in Kien My village, Kien Thanh hamlet, Quy Nhon district, now located in block 1 of Phu Phong town, Tay Son district, Binh Dinh province. On November 16, 1988, the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism issued a decision to recognize Go Da Den as a historical-cultural relic. Kien My is not only a place where Tay Son leaders were attached from childhood to adulthood but also one of the early bases of the Tay Son movement. In 1771, after a period of preparing forces, Nguyen Nhac, along with Nguyen Hue and Nguyen Lu, raised an uprising flag in Tay Son Thuong Dao. In 1773, from the Upper Dao insurgents marched down to liberate the lower Tay Son region and stationed their headquarters in Kien Thanh hamlet, the center of which was Kien My hamlet. This was a wise decision, especially in the early days when the uprising was launched and the force was not yet strong. On the one hand, because this is the homeland of the insurgent leaders, but on the other hand, also very important, is the favorable location of Kien My. Located at the foot of An Khe Pass on the left bank of the Kon River, Kien My is a convenient waterway transportation hub. From Kien My, you can take the road through An Khe, follow the waterway up the river to the Thuong people area, or down to the delta, to the coast. After a short period of consolidating their forces, the insurgent army moved down from Kien Thanh hamlet to capture Quy Nhon citadel, creating a turning point in the entire development process of the uprising. Kien My village - Kien Thanh hamlet, as the headquarters and starting point of the insurgent army moving to liberate the delta, has a very important position. On Kien My land, there are still many historical relics associated with the Tay Son leaders as well as the entire Tay Son movement. In addition to the ancient tamarind tree and ancient well, Truong Trau Wharf also has Palace Garden, Tap Binh Palace, Cam Co Palace, Da Den Hill, and Cut Cu Hill, which are places that reflect the headquarters and barracks of the insurgent army. Go Da Den is a high and wide land. This is originally a wild forest with an estimated area of about 5 hectares stretching from Phu Lac to Bau Dao. In the middle of the mound emerges a very large black rock, that's why people call this mound Black Stone Mound. Time, war, and the revenge of the Nguyen Dynasty, partly because the insurgents stopped here not long ago, so now there are traces associated with the activities of the insurgents, in addition to the places preserved in folk memory. , there is almost nothing left. The area of Da Den mound was reduced to only 2 hectares, because people dug up the soil to make bricks and used stones to build houses. The large black rock has also been chipped into pieces. Source: People's Committee of Tay Son District, Binh Dinh Province
Gia Lai 4799 view
Ben Truong Trau
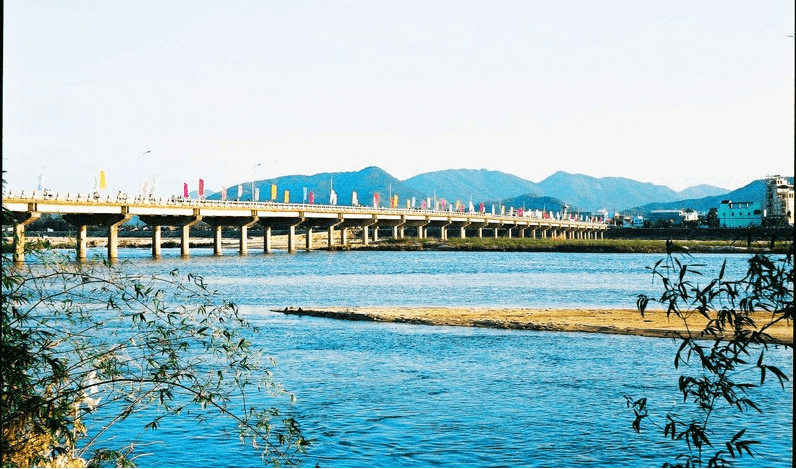
Truong Trau Wharf is a large betel trading wharf on the banks of the ancient Con River, in Trau hamlet, Kien My village, about 200m from Tay Son Tam Kiet temple. Betel and areca nuts are a famous product of both the upper and lower Tay Son regions, especially the type of betel grown by the Upper People in the Central Highlands. Truong Trau Wharf became a place of transit and trade relations between the mountains and the plains, in addition to betel and areca nuts, there were also many other essential goods. When Mr. Ho Phi Phuc's family still resided in his wife's hometown - Phu Lac village, in addition to farming, they also participated in trade with the lowlands and uplands, thus becoming rich. His children also continued their father's career, maintaining and expanding trade and exchange. Ben Truong Trau, with its trading exchanges, had a great influence on the uprising career of the three Tay Son brothers, especially Nguyen Nhac. Nguyen Nhac often traveled back and forth to the upper Tay Son region, had close relationships with ethnic minorities in the Central Highlands, and traded with markets, wharves, and towns in the delta. This helped him expand his vision and understand the suffering of people from all walks of life, thereby easily mobilizing and uniting forces to participate in the uprising. After preparations at the upper Tay Son, the Tay Son insurgents under the command of Nguyen Nhac launched a large-scale operation to liberate the lower Tay Son, liberated the Quy Nhon government, and laid a solid foundation. for the movement's next victories. Among that achievement, Ben Truong Trau was an important focal point, where information and correspondence of the insurgent army was connected in the early days of preparing for the uprising, until it reached its peak. Legend has it that next to the old Truong Trau Wharf, Nguyen Nhac built a house to store betel and serve as an inn for betel traders. Therefore, the people of Kien My, as well as many surrounding areas, know Nguyen Nhac as Mr. Hai Trau. After the Tay Son dynasty passed away, Kien My people built on the old house's foundation a temple to worship the three Tay Son brothers, called Vinh Tho temple (also called Cay Gon temple because there is a big tree here). Later, the French colonialists used it as a food warehouse and then destroyed it. In 1963, three Southern mendicants and local people built a small thatched pagoda (on the old temple foundation). In 1967, it was newly built with bricks called Ngoc Binh Vihara. Truong Trau Wharf has now been filled in, only a sandy beach along the river, no longer crowded with boats and the hustle and bustle of preparing for a great career, but "The old tamarind tree, the old Ben Trau..." has go down in history, forever echoing a glorious time. Source: People's Committee of Tay Son District, Binh Dinh Province
Gia Lai 4130 view
Tay Son Tam Kiet Temple
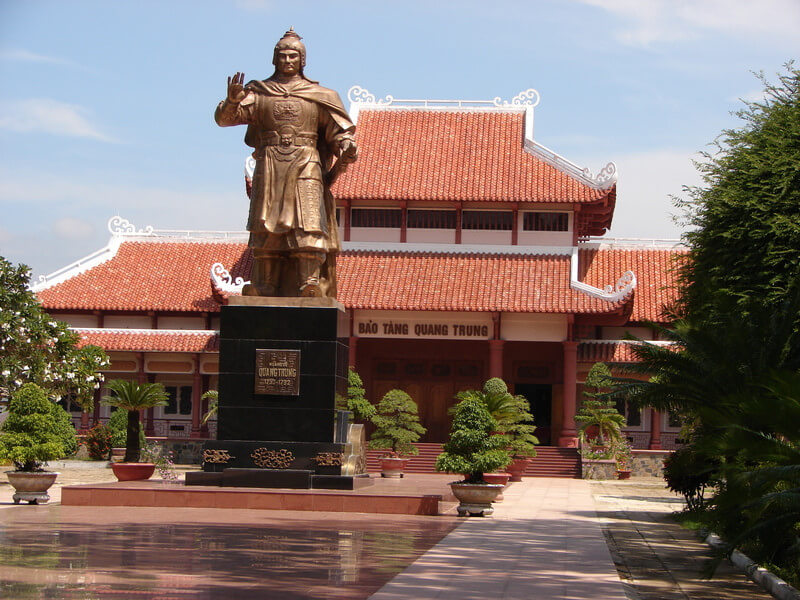
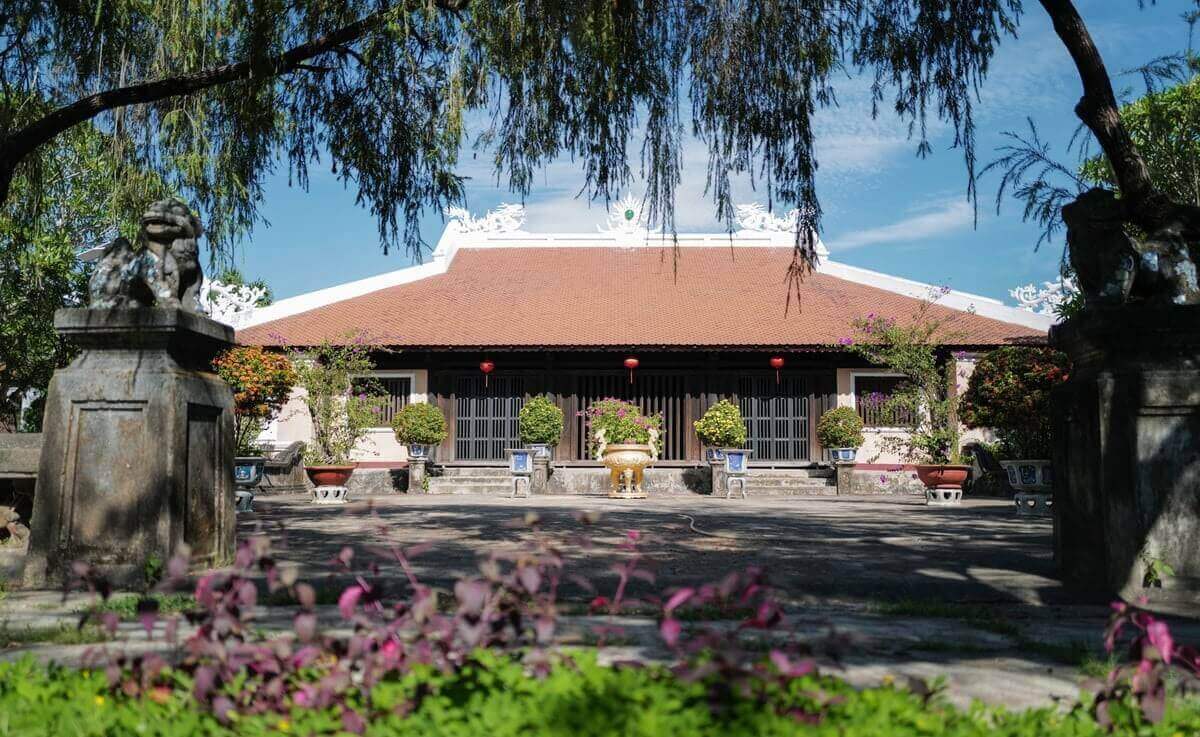
The Tam Kiet Tay Son Temple relic area includes 2 relics: Tay Son Palace and Truong Trau wharf site, located in Phu Phong town, Tay Son district, Binh Dinh province. associated with the names of three brothers Nguyen Nhac, Nguyen Hue and Nguyen Lu, leaders of the Tay Son movement, Tay Son dynasty at the end of the 18th century; decided to be classified as a special national monument by the Prime Minister on December 31, 2014). Historical sources say that the ancestors of the Tay Son Dynasty were originally from the Ho family in Hung Nguyen district, Nghe An. Come to rest in Tay Son Nhat hamlet, Quy Ninh. Nguyen Nhac's father, Mr. Ho Phi Phuc, and his wife, Ms. Nguyen Thi Dong, moved to Kien My village (now block 1, Phu Phong, Tay Son, Binh Dinh) to live for business purposes. Kien My village is also a gathering place for martyrs and the first base of the peasant movement in the lower Tay Son region. Nguyen Nhac and his two younger brothers, Nguyen Hue and Nguyen Lu, led the Tay Son uprising to bring Nguyen Hue and Nguyen Nhac to the throne. After the fall of the Tay Son dynasty, the house of Mr. and Mrs. Ho Phi Phuc's family in Kien My village was burned and razed. Some time later, right on the old house's foundation, local people contributed their contributions to build a tall and majestic communal house to secretly worship Tay Son Tam Kiet, named Kien My village communal house. In 1946, the communal house burned down. In 1958 - 1960, Binh Khe people once again built a new temple named Tay Son Palace, officially worshiping the three Tay Son brothers and holding an anniversary festival. commemorate every year. Tay Son Dien is built in the style of Dinh, with split stone foundations, solid brick walls, and cement tiled roof, with an area of over 100 square meters. The main shrine has three compartments, in the middle worships Emperor Quang Trung - Nguyen Hue, on the right worships Emperor Thai Duc - Nguyen Nhac, on the left worships Dong Dinh Vuong - Nguyen Lu, on the left and right the shrine worships military mandarins and ancestors. In the Tay Son family, the two gables have gongs and drums to serve ceremonies. In 1998, the State built and expanded Tay Son Palace. The temple was rebuilt with ancient architecture, quite large and majestic, three times the area of the old temple, made of reinforced concrete, Recreating the large, well-structured columns like an old communal house, the roof is cast in concrete, and covered with funny-nosed scale tiles. In front of the main temple, there is a pavilion like the old temple, on both sides there are two rows of large columns decorated with majestic dragons wrapped around the columns. In front of the house is a red granite stele with a summary of the temple's history. The Electric Gate remains the same. The well site was embellished with a hexagonal shelter, a concrete roof covered with scale tiles, and the surrounding Tamarind tree was also renovated more spaciously than before. In 2004, nine ceramic statues were brought back, covered in real gold on the outside, and placed in the inner sanctum. The rear hall has 3 altars, in the middle is the altar worshiping Emperor Quang Trung - Nguyen Hue; On the right is the altar worshiping Emperor Thai Duc - Nguyen Nhac; On the left is the altar of Dong Dinh Vuong - Nguyen Lu. Behind the altars is a large wooden diaphragm with carved dragons, patterns and gilded lacquer. In front, on both sides of the three altars, there are two wooden shelves holding eight sets of weapons. On the East and West sides of the inner palace, there are altars to worship civil servants, gods, and military generals of the Tay Son period. Although Tay Son Palace has gone through ups and downs over the years, it has been preserved, preserved and promoted by local people for generations to commemorate and pay tribute to the great contributions of national hero Quang Trung. – Nguyen Hue in his career of fighting to build and defend the country. Source: Department of Culture and Sports of Binh Dinh Province
Gia Lai 7371 view
Historical site of collective grave of martyrs of the Golden Star Division
The relic is a mass grave in Tay Phuong Danh area, Dap Da ward, An Nhon town, the resting place of 153 soldiers of Battalion 6, Regiment 12, Golden Star Division who died in the General campaign. offensive and uprising in the Spring of Mau Than 1968. Opening the 1968 Spring Mau Than campaign, in An Nhon area, from December 25, 1967 to January 17, 1968, provincial and district soldiers and guerrilla forces coordinated to attack the enemy in many places, causing them harm. much damage. Battalion 6, Regiment 12, Sao Vang Division of Military Region 5 was assigned the task of fighting the enemy in areas close to the provincial capital, attracting the enemy to the countryside so that the liberation army could attack Quy Nhon town. After attacking the Phu Cat training center on January 19, 1968, the Battalion destroyed the enemy holding the Sita - Nhon Hung bridge on Highway 1. Fearing the loss of Dap Da, the district capital of An Nhon and Quy Nhon will be threatened, the enemy has sent here a regiment of South Korean soldiers, 4 security companies, 32 tanks and armored vehicles to surround Battalion 6 and use artillery to counterattack. With superior military and weapons superiority, the enemy drove the people out, trying to surround and isolate the soldiers of Battalion 6 in the Tay Phuong Danh area to destroy them. The unit fought bravely with the enemy for 5 days and nights, from January 20, 1968 to January 24, 1968 until there were no more bullets left, the soldiers used hoes, shovels, and bayonets to attack with armor. fought with the enemy and sacrificed heroically. Admiring the tenacious fighting spirit, courage and indomitable sacrifice of the soldiers of Battalion 6, the People, despite the danger, buried 153 soldiers' bodies in a mass grave in the Tay Phuong Danh area - Smashing Rocks in infinite grief. People around the area call it Ma To. The mass grave of soldiers of Battalion 6, Regiment 12, Golden Star Division was ranked as a provincial revolutionary relic by the Provincial People's Committee on October 20, 2003. In 2016, the collective grave of soldiers of Battalion 6, Regiment 12, Golden Star Division was invested in many renovation items: building an incense house, carving stone tombstones, covering the entire grave with granite, and making a yard. The garden creates a clean and beautiful landscape, expressing the people's affection for the relatives of the Northern martyrs who fought and sacrificed for the South. Binh Dinh Provincial Museum is preparing a document to request the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism to upgrade it to the national level to match the historical value of this relic. Source: Binh Dinh Province Electronic Information Portal
Gia Lai 7110 view
Ancient Go Sanh ceramic kiln
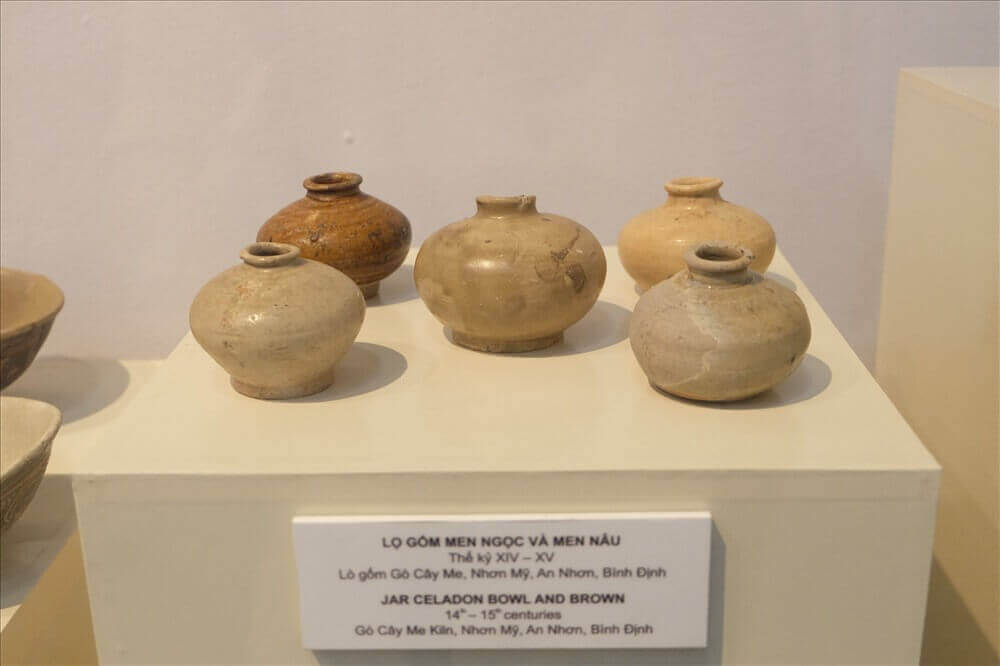
Go Sanh or Sanh hamlet is the name of a small hamlet in Phu Quang village, Nhon Hoa ward, An Nhon town. Phu Quang people say that while digging land for construction or farming, they often come across areas thick with intact pieces of ceramics of many types such as bowls, plates, and cups. Around the 70s, Go Sanh ceramics followed antique dealers to many regions and attracted the attention of ancient ceramic researchers in Vietnam and the world. In March 1974, an archaeological team from Saigon came to Phu Quang to research. Although there have been no excavations at Go Sanh, they have hypothesized that the owners of Go Sanh pottery are Cham people. From the above information, the Hanoi Institute of Archeology and Binh Dinh General Museum have planned a long-term research program at Go Sanh and all ancient ceramic relics in Binh Dinh. Until 2000, there were 4 excavations continuously conducted at this relic site. Up to now, Binh Dinh pottery kilns have 5 groups. In An Nhon town, there are Go Sanh, Go Cay Ke, and Go Hoi. All of these relics are located along the banks of the Kon River flowing into Thi Nai Bay (Quy Nhon port today) - a convenient location for waterway transportation. Archaeological excavations at Go Sanh were carried out in 1991, 1992, 1993. In 1994, besides Vietnamese scientists, there was additional cooperation from Japanese scholars. Among the kiln sites that have been identified in 5 locations within the former Vijaya region, kilns No. 1, No. 2 and 3 are in Go Sanh. Furnace number 1: Named Cay Quang furnace. The kiln is still quite intact, from the kiln wall, kiln floor and the final fired product of this kiln. The furnace has a tubular shape with a total length of 14m. The furnace chamber is rectangular, gradually expanding towards the end, measuring 1.6m; The width at the front is 2.8m; at the rear and an additional 10m in length. On one side of the oven wall there is a door for loading and unloading products. Furnace number 2: It is called Cay Man furnace (Roi Tree). The kiln area is located in the south of Go Sanh. Technically similar to furnace No. 1 (Cay Quang furnace), the furnace wall is also built of compacted soil bags and the arrangement of fire sharing columns in the burner is similar. Furnace No. 3: Located under furnace No. 2. According to researchers, this is the furnace with the earliest construction date. The wall of furnace No. 3 is not made of burnt shell material but is completely made of earth. The furnace is 1.2m wide near the burner, 1.7m wide at the back. The length of the furnace body is 5.3m. Currently, the Binh Dinh Provincial General Museum collects and preserves a quite rich collection of Go Sanh ceramic products. Porcelain products mainly produced here include enameled bowls, plates, pots, unglazed tiles and architectural decorations. Celadon enameled dishes and brown enameled jars show similar characteristics to the products of Fujian kilns (China). Recent information shows that Go Sanh Binh Dinh ceramics are produced not only for local service but also to participate in the export market to countries in Southeast Asia and further afield, Egypt. Among the artifacts found on the shipwreck in the Calatagan archipelago off Pantanan Island in the Philippines are thousands of Go Sanh ceramics. Some Vietnamese experts believe that the beginning of Binh Dinh ceramic production may have started from the late 13th to the 14th century, or at the latest until the 16th century. The owners of Go Sanh pottery kilns and other ancient pottery kilns in Binh Dinh are none other than the ancient Champa people. Go Sanh pottery kiln archaeological relic site has been ranked by the State as a National Historical-Cultural Relic. Source: Website of An Nhon Town People's Committee
Gia Lai 4498 view
Thap Thap Pagoda
Di Da Thap Thap Pagoda is located in Van Thuan village, Nhon Thanh ward, An Nhon town, Binh Dinh province. The name of the pagoda "Thap Thaps" is because previously there were 10 Cham towers on this hill, which later collapsed. The name "Amitabha" is the title of the Buddhist leader of the Pure Land. Amitabha also means reason, the original awareness of sentient beings. Combining the above meanings, the ancestral temple is named Thap Thap Amitabha Temple. Thap Thap Di Da Ancestral Pagoda is associated with the name of the founder, Zen Master Nguyen Thieu. Many documents today indicate that his surname was Ta, self-named Hoan Bich, from Trinh Huong district, Chaozhou district, Guangdong province, China. He was born in the year of the Rat (1648), and at the age of 19 became a monk at Bao Tu Pagoda. In 1677, he followed a Chinese trading boat to Quy Ninh district, now in Binh Dinh province, about 28 km from Quy Nhon city, and built a hermitage to worship Amitabha Buddha. In 1683, the pagoda used bricks and stones from 10 fallen towers to build the pagoda. The pagoda has gone through 16 generations of lineage with many famous Zen masters such as: Zen Master Lieu Triet, Zen Master Minh Ly, Zen Master Phuoc Hue... Zen Master Phuoc Hue has been honored as National Master. He was invited to preach sutras in the Nguyen royal palace from the reign of King Thanh Thai to King Bao Dai, and taught Buddhism at Truc Lam and Tay Thien Buddhist schools (Hue) since 1935. From outside, walking along the lotus pond to the temple gate, there are two tall square pillars, on top of which are placed two lion statues sitting majestically, connecting an arc, above are attached two words "Thap Thap". Behind the gate is a screen with an embossed dragon and horse symbol placed on a kneeling pedestal. The main hall was rebuilt by Zen Master Lieu Triet in 1749. Today's main hall has a straight roof, yin-yang tiles, and two dragons with pearl paintings on the roof. The Buddha hall is decorated solemnly, in the middle worshiping statues of Tam The Buddha, Chuan De, Ca Diep, and Ananda; The shrine worships Avalokiteśvara Bodhisattva and Ksitigarbha Bodhisattva, placed in two compartments on either side of the Buddha hall; On the left and right walls, there are statues of Thap Bat La Lan, statues of Thap Dien Minh Vuong, Dharma Protector, Patriarch Dat Ma and Patriarch Ty Ni Da Luu Chi. Most of the worship statues were carved during the reign of Zen Master Minh Ly (1871-1889). The pagoda was given a sign by Lord Nguyen Phuc Chu "Sac Tu Thap Amitabha Pagoda" hanging in the middle of the main door of the main hall, which was engraved by Venerable Mat Hoang in 1821. The big bell (cast in 1893) and the big drum were placed. at both ends of the hallway. Behind the main hall, there is a stele inscribed with the poem "Thap Thap Amitabha Pagoda" written by layman Duong Thanh Tu and founded by Venerable Minh Ly in 1876. The monk's house is located behind the main hall built by National Master Phuoc Hue in 1924. The Patriarch's house is in the south, connecting the main hall and the monk's house, worshiping the Patriarch of Khai Son Nguyen Thieu and the late abbots and monks. and past Buddhists. Opposite the Patriarch's house is the lecture hall, there is a wooden board with the article "Thap Thap Tu Chi" written by An Nhon Academician Vo Khac Trien in 1928, recording the history of enlightenment, the process of construction and inheritance. of Thap Thap ancestral temple. In particular, Binh Dinh Newspaper said that the pagoda still retains 2,000 wood carvings used to print the Amitabha Sutra, Diamond Sutra, Lotus Sutra, etc. The Tripitaka offered by Governor Ha Tien Mac Thien Tu also exists. 1,200 volumes of sutras, laws, treatises and records. The pagoda also preserves the Korean Tripitaka and the Taiwanese Tripitaka. The Patriarch Tower Garden is located in the North with 20 ancient towers containing the bodies of the abbots and monks in the temple. Behind the pagoda, there is also the White Tiger tower and the Council tower The pagoda has been recognized by the Ministry of Culture as a national historical and cultural relic. Amitabha Thap Thap Pagoda is the most famous pagoda in the Central region. Source: Website of An Nhon Town People's Committee
Gia Lai 4368 view
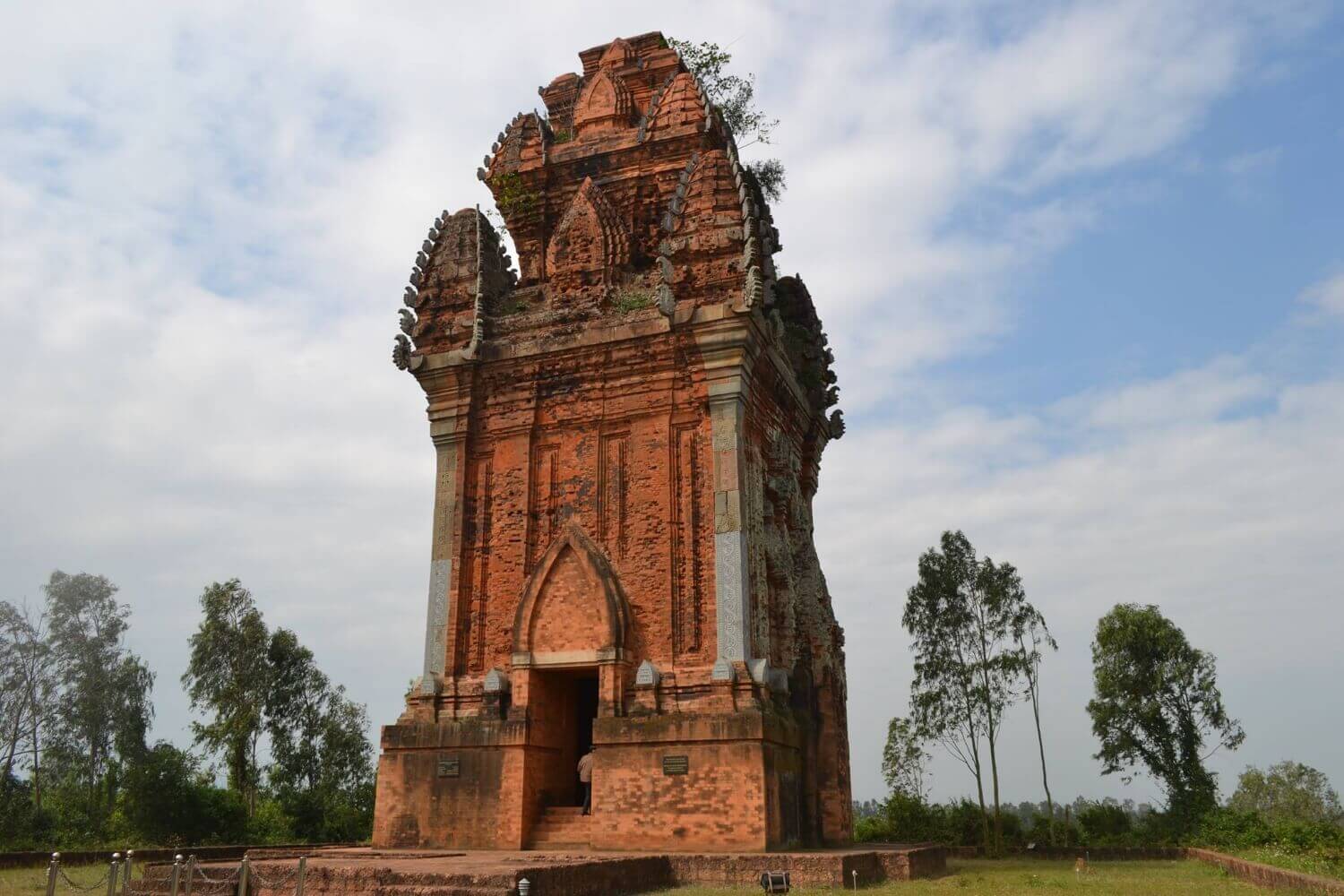
Canh Tien Tower
Canh Tien Tower is located on top of a not very high hill in the center of Do Ban citadel, the ancient capital of the Champa kingdom in Nam An village, An Nhon town. In the book Dai Nam Nhat Thong Chi, it is written: "An Nam ancient tower in Nam An village, Tuong Van district, in Do Ban citadel, is commonly called Canh Tien tower. From the shoulder of the tower up, all four sides look like fairy wings, so it's called that name." French researchers, in their own way, call it Tour de Cuvre (Bronze Tower). Towers are a popular architectural form of Champa culture. In Cham language, there is a common word for this type of architecture: Kalan (temple). The main function of Kalan, as the word implies, is to serve spiritual life and religious rituals. However, the tower's architecture is deeply artistic and is a work in which artisans express their talent and creativity, so it is less constrained by religious rituals. Among them, Canh Tien is a beautiful tower, uniquely shaped and elegant with a very reasonable layout. The tower was built tall and imposing on a nearly square plane, each side about 10 meters long with staggered ramps. The entire tower is about 20m high, all four sides around the tower's body are decorated with wall pillars, protruding in a harmonious ratio with the overall architecture. The corners of the tower body are made of large stone blocks so it is quite sturdy. In terms of form, the tower has 4 soaring pointed arch doors opening in 4 directions, but only the main door facing east is connected to the heart of the tower, the rest are 3 fake doors. The slightly protruding frill forms a support for the corner towers above. The carved images are mainly concentrated on the roof. With four existing floors, each floor has 4 decorative corner towers, each corner has small floors, creating a leaf shape that gradually gets smaller towards the top, creating the feeling of birds in flight. Perhaps it is because of this appearance that people let their imagination run wild, associated with the image of a fairy and named the tower Canh Tien. The carved stones in the shape of a phoenix tail mounted on the floors of the fake tower and the image of Makara, a sea monster in Indian mythology with sharp fangs and a long trunk, decorating the corners of the walls give Canh Tien tower a beautiful look. Luxurious, mysterious. Unlike many Cham towers, the decoration of Canh Tien tower is elaborate to the point of perfection. From the door arch system to the flexible, symmetrically layered spiral pattern strips to the delicately carved stone blocks forming connected patterns, all exude a beauty that is both elegant, elegant, and majestic. suspicious, superficial. It is also possible that due to its graceful beauty, the tower also has the folk name of Daughter tower. According to ancient documents, Do Ban citadel was built by Champa king Ngo Nhat Hoan in the 10th century, while Canh Tien tower was built in the 12th century, under the reign of King Che Man (Jaya Sinbavarman III). Perhaps this is the Che Man tower dedicated to Queen Paramecvari, Princess Huyen Tran, the noble Vietnamese girl who put her interests first and formed a historic relationship with him. Legend has it that before leaving Dai Viet, the Tran Dynasty's princess with jade leaves and golden branches learned thoroughly all royal rituals and Champa folk activities. Working as a bride far from home, she was loved and respected by her subjects because this Vietnamese queen not only spoke Champa language fluently, knew how to sing and dance Champa folk songs, but also took the trouble to teach the royal palaces. Women and subjects from their husband's hometown weave cloth, grow rice, embroider, and sew. It is not an exaggeration to say that: Marrying Huyen Tran, Che Man's bride price was the two continents O - Ly, and Canh Tien Tower was the love gift he gave her, as a sacred recognition of his people. . Source: Website of An Nhon Town People's Committee
Gia Lai 5965 view
Citadel Emperor
Emperor Citadel is located in Nhon Hau commune and Dap Da ward, An Nhon town, 27km northwest of Quy Nhon. Emperor Citadel was built by the Tay Son dynasty in 1776 on the basis of Do Ban citadel left by the Champa Kingdom and was officially named Emperor Citadel since 1778. During a long period from 1776 to 1793, The citadel was the headquarters of the Tay Son army and later the capital of the central government of Emperor Thai Duc - Nguyen Nhac. The Imperial Citadel was originally a rectangular architectural complex, consisting of three citadels: the Outer Citadel, the Inner Citadel and the Forbidden Citadel. The outer citadel has a circumference of 7400m. The Citadel, also known as the Imperial Citadel, has a rectangular shape of 430m long and 370m wide. Inside the Citadel is the Forbidden City, also rectangular, 174m long and 126m wide. Through many excavations, many architectural works have been revealed, proving that the Thai Duc dynasty developed on this land. That is the main hall's floor, the octagonal floor with Bat Trang tiles and Champa white stone. The two semi-circular lakes are symmetrical around the octagonal palace, with rows of coral stones and stone steps attached to the lake. In addition to two semicircular lakes, the excavation also revealed a heart-shaped lake. Hundreds of years old fig trees next to Gia Son island. The square well at the corner of the citadel is paved with laterite, but the water is still clear to this day even though over time the plants and trees accidentally cover it. The Imperial Citadel also witnessed battles between the Tay Son and Nguyen dynasties, including the siege battle between the two Tay Son generals, Tran Quang Dieu, Vo Van Dung, and general Vo Tanh in May 1801. Unable to resist the Tay Son army, Vo Tanh self-immolated along with the civil servant Ngo Tung Chau, who drank poison and committed suicide. After the fall of the Tay Son Dynasty, this place became a place to worship the "twin faithful" Vo Tanh and Ngo Tung Chau. Although the Imperial Citadel is only a historical relic, the culture and craft villages around the citadel are still the same as ever. Not as many as the "36 streets" of Thang Long citadel, but around the Emperor Citadel there are still many craft villages bustling with production such as Van Son pottery village, Phuong Danh weaving village, Bang Chau bronze casting village, wood turning village, etc. hats... show a bustling capital with horses, carriages and prosperity, making us feel uneasy thinking about an ancient legend. The citadel was recognized by the Ministry of Culture and Information as a national monument in 1982. Source: Website of the People's Committee of An Nhon town
Gia Lai 4164 view